Example script illustrating the third dataset
Contents
Load in the third dataset
load('dataset03.mat');
whos
Name Size Bytes Class Attributes
betamn 1323x156 1651104 double
betas 1323x156x30 49533120 double
betase 1323x156 1651104 double
glmr2 1323x1 10584 double
hrfmn 1323x38 402192 double
hrfs 1323x38x30 12065760 double
hrfse 1323x38 402192 double
meanvol 64x64x22 720896 double
roi 1323x1 10584 double
roilabels 1x12 1408 cell
tr 1x1 8 double
vxs 1323x1 10584 double
vxsselect 1323x3 3969 logical
Inspect the data at a gross level
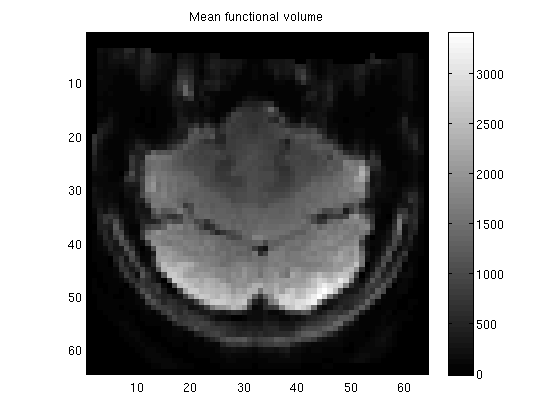
figure;
imagesc(meanvol(:,:,11));
axis equal tight;
colorbar;
title('Mean functional volume');
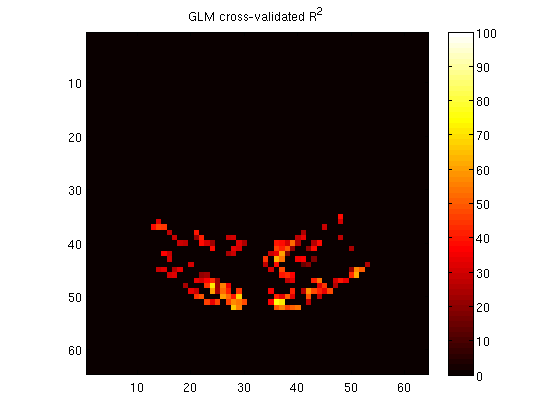
vol = zeros(size(meanvol));
vol(vxs) = glmr2;
figure;
imagesc(vol(:,:,11),[0 100]);
colormap(hot);
axis equal tight;
colorbar;
title('GLM cross-validated R^2');
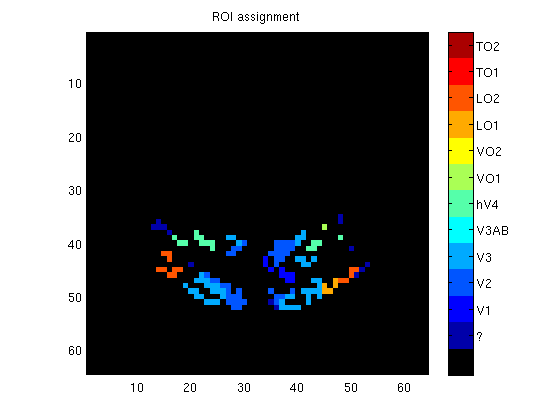
vol = zeros(size(meanvol));
vol(vxs) = roi;
figure;
imagesc(vol(:,:,11),[0-.5 12+.5]);
colormap([0 0 0; jet(12)]);
axis equal tight;
cb = colorbar;
set(cb,'YTick',1:12,'YTickLabel',roilabels);
title('ROI assignment');
Inspect the estimated HRF and beta weights for one voxel
goodvoxels = find(glmr2 > 70);
ii = goodvoxels(1);
fprintf('The chosen voxel is the %dth voxel of the %d voxels contained in the data file.\n',ii,length(vxs));
fprintf('The absolute index of this voxel is %d.\n',vxs(ii));
fprintf('The ROI assignment is %s.\n',roilabels{roi(ii)});
fprintf('The GLM R^2 for this voxel is %.1f.\n',glmr2(ii));
The chosen voxel is the 203th voxel of the 1323 voxels contained in the data file.
The absolute index of this voxel is 26926.
The ROI assignment is V1.
The GLM R^2 for this voxel is 72.2.
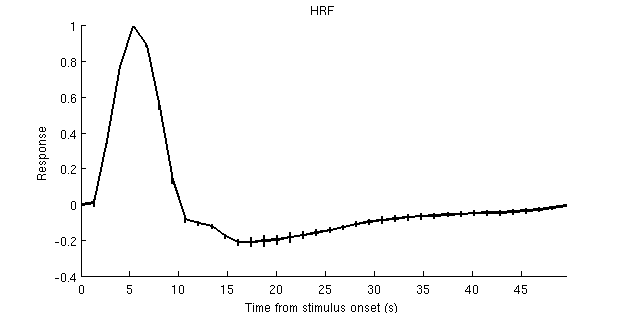
figure; hold on;
set(gcf,'Units','points','Position',[100 100 500 250]);
xx = 0:tr:tr*(size(hrfmn,2)-1);
yy = hrfmn(ii,:);
ee = hrfse(ii,:);
plot(xx,yy,'k-','LineWidth',2);
for p=1:length(yy)
plot([xx(p) xx(p)],[yy(p)-ee(p) yy(p)+ee(p)],'k-','LineWidth',2);
end
ax = axis; axis([xx(1) xx(end) ax(3:4)]);
xlabel('Time from stimulus onset (s)');
ylabel('Response');
title('HRF');
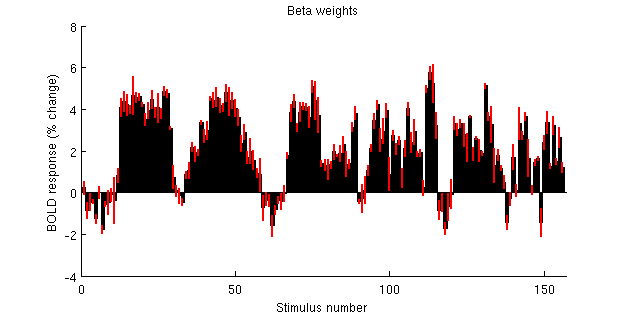
figure; hold on;
set(gcf,'Units','points','Position',[100 100 500 250]);
n = size(betas,2);
yy = betamn(ii,:);
ee = betase(ii,:);
bar(1:n,yy,1);
for p=1:n
plot([p p],[yy(p)-ee(p) yy(p)+ee(p)],'r-','LineWidth',2);
end
ax = axis; axis([0 n+1 ax(3:4)]);
xlabel('Stimulus number');
ylabel('BOLD response (% change)');
title('Beta weights');